Python and JSON
Why learn about JSON
Back when my team was working on an app for Dublin bus I had to make a machine learning model and obviously we needed a dataset, unfortunately, there were no useful databases. Luckily I was provided with a REST API which can give me the real-time bus information. A REST API is basically a server which can send us information via an HTTP request. The data in most cases will be in XML or JSON. Now all I needed to do make a scrapper in python using a crone scheduler to run scrapper for a couple of months to get enough data. The only problem was that I didn’t know much about JSON and just by fumbling around I somehow managed to get all data I need. Now coming to present I had a similar project based on Dublin bus but here an API request generated JSON files size of mountains and I couldn’t hack my way through this. Therefore I set out to study about it and create a note for future reference. Case and point JSON is datatype most of us will encounter in our work.
JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation just because it has javascript mentioned on it doesn’t mean its exclusive to JS. Infact most programs support it and use for data transfer espcially via API request. One good thing about JSON is that as a user the data is easily readable.
A simple JSON looks like this:
{
"employee":
{
"name": "sachin",
"salary": 56000,
"location": "Dublin"
}
}If you look at this example it almost looks like a python dictionary. It uses key:value pair system which we use in dictionaries. If you look at the example we see a key called “name” with a corresponding value as “sachin”. JSON supports most of the primitive data types which we use like list, strings and arrays. Infact we can have nested arrays, objects or dictionaries. Example above we have a dictionary with key “employee” which has value in form of nested dictionary. One thing to note is that when we get data in JSON format from some server it may not always look pretty for example look at the JSON i got from an API call I make.
{"errorcode":"0","errormessage":"","numberofresults":9654,"timestamp":"18\/06\/2020 23:35:53","results":[{"stopid":"2","displaystopid":"2","shortname":"Parnell Square","shortnamelocalized":"Cearnóg Parnell","fullname":"Parnell Square","fullnamelocalized":"","latitude":"53.3522411111","longitude":"-6.263695","lastupdated":"08\/06\/2020 10:29:55","operators":[{"name":"bac","operatortype":1,"routes":["38","38A","38D","38B","46A","46E"]}]This JSON without intendation is difficult to read by humans. One thing to do is to put these outputs into a JSON beautifier sites in the internet where it will indent the file so that we can easily read it.
Since JSON is pretty important. Python has a package to deal with such data and one more cool thing is that we can parse JSON like a normal python object like a list which means I can use JSON on stuff like Matplot and get plots out of it.
import jsonThere are two important concepts which we should be aware of when working with JSON and python serialization and deserialization
serializationis the conversion of a python object to a JSON format.deserializationis the conversion of JSON data to python object like a dictionary or string.
Serialize to JSON data
As mentioned earlier python has json library. In it there are two important functions for serializations dump() and dumps().
-
dump(): dump is used to write the data we have into a file; we can convert python datatypes to JSON equivalent and write it into a file. -
dumps(): dumps on other hand is used to make a string equivalent of the object in JSON format so we can print it and see the result. Something similar to __ str __ or to_String() in java. Look at the following table from the python docs
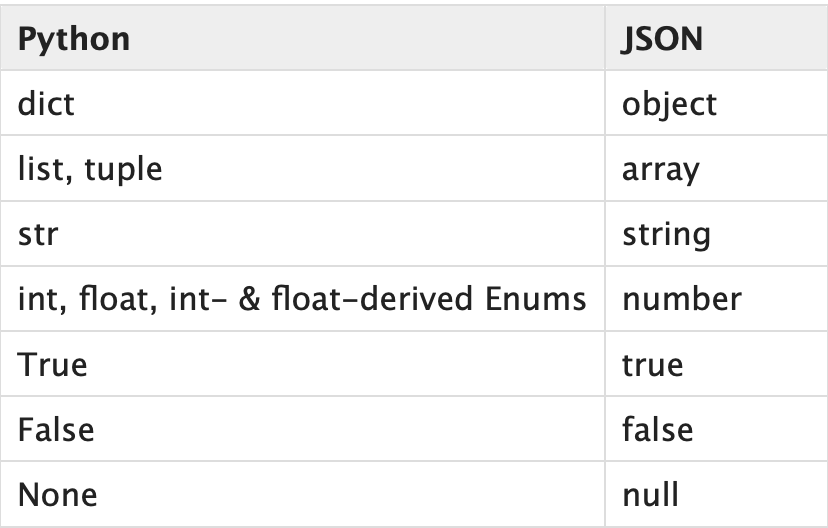
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
import json
data_to_convert = { "employee": { "name": "sachin" ,"salary": "50000" , "age" :24 } }
with open("file_to_write.json","w") as file:
json.dump(data_to_convert,file,indent = 4)
json_to_string = json.dumps(data_to_convert,indent = 4)
print(json_to_string)
Explaination :
- First we import the json library
- next we open a file with write access
- use
json.dump()to convert the dictionary to a json object and write to file - print the json object by creating a json string using dumps() and output the result
If you notice there is an additional parameter called indent used this makes json output in a more human readable form.